MATLAB Examples 4 (covering Statistics Lecture 7)
Contents
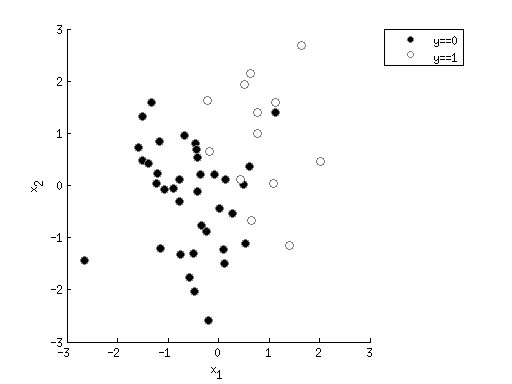
Example 1: Simple 2D classification using logistic regression
x1 = randn(50,1);
x2 = randn(50,1);
y = (2*x1 + x2 + randn(size(x1))) > 1;
figure; hold on;
h1 = scatter(x1(y==0),x2(y==0),50,'k','filled');
h2 = scatter(x1(y==1),x2(y==1),50,'w','filled');
set([h1 h2],'MarkerEdgeColor',[.5 .5 .5]);
legend([h1 h2],{'y==0' 'y==1'},'Location','NorthEastOutside');
xlabel('x_1');
ylabel('x_2');
options = optimset('Display','iter','FunValCheck','on', ...
'MaxFunEvals',Inf,'MaxIter',Inf, ...
'TolFun',1e-6,'TolX',1e-6);
logisticfun = @(x) 1./(1+exp(-x));
X = [x1 x2];
X(:,end+1) = 1;
params0 = zeros(1,size(X,2));
paramslb = [];
paramsub = [];
costfun = @(pp) -sum((y .* log(logisticfun(X*pp')+eps)) + ...
((1-y) .* log(1-logisticfun(X*pp')+eps)));
[params,resnorm,residual,exitflag,output] = ...
lsqnonlin(costfun,params0,paramslb,paramsub,options);
Warning: Trust-region-reflective algorithm requires at least as many equations
as variables; using Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm instead.
First-Order Norm of
Iteration Func-count Residual optimality Lambda step
0 4 1201.13 544 0.01
1 8 249.865 66.7 0.001 1.57413
2 12 162.838 16.1 0.0001 3.09029
3 22 157.936 10.8 100 0.168952
4 26 155.321 7.6 10 0.120881
5 30 153.054 14.6 1 0.91166
6 36 148.397 7.02 100 0.173822
7 40 147.149 3.24 10 0.090581
8 45 146.815 1.57 100 0.046862
9 49 146.718 1.02 10 0.0248996
10 54 146.682 0.807 100 0.01455
11 58 146.665 0.669 10 0.00997112
12 62 146.643 0.809 1 0.0786498
13 68 146.624 0.377 100 0.0113596
14 72 146.619 0.206 10 0.00539815
15 77 146.618 0.12 100 0.00271585
16 81 146.618 0.0742 10 0.00154244
17 86 146.618 0.062 100 0.00104312
18 90 146.617 0.0539 10 0.000814137
Local minimum possible.
lsqnonlin stopped because the final change in the sum of squares relative to
its initial value is less than the selected value of the function tolerance.
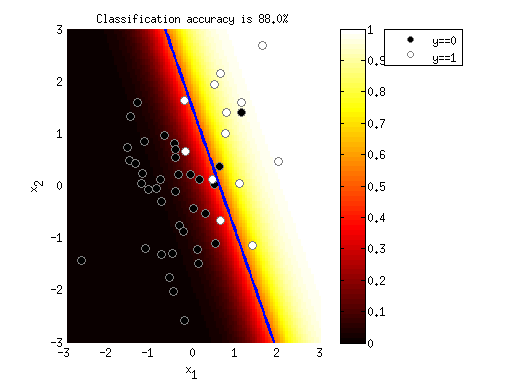
modelfit = logisticfun(X*params') >= 0.5;
pctcorrect = sum(modelfit==y) / length(y) * 100;
ax = axis;
xvals = linspace(ax(1),ax(2),100);
yvals = linspace(ax(3),ax(4),100);
[xx,yy] = meshgrid(xvals,yvals);
X = [xx(:) yy(:)];
X(:,end+1) = 1;
outputimage = reshape(logisticfun(X*params'),[length(yvals) length(xvals)]);
h3 = imagesc(outputimage,[0 1]);
set(h3,'XData',xvals,'YData',yvals);
colormap(hot);
colorbar;
[c4,h4] = contour(xvals,yvals,outputimage,[.5 .5]);
set(h4,'LineWidth',3,'LineColor',[0 0 1]);
uistack(h3,'bottom');
uistack(h4,'top');
axis(ax);
title(sprintf('Classification accuracy is %.1f%%',pctcorrect));
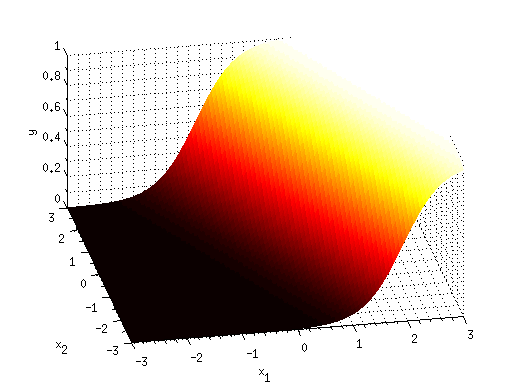
figure; hold on;
h1 = surf(xvals,yvals,outputimage);
set(h1,'EdgeAlpha',0);
colormap(hot);
xlabel('x_1');
ylabel('x_2');
zlabel('y');
view(-11,42);
set(gca,'XGrid','on','XMinorGrid','on', ...
'YGrid','on','YMinorGrid','on', ...
'ZGrid','on','ZMinorGrid','on');
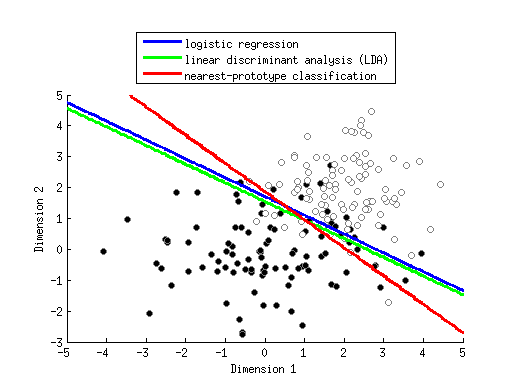
Example 2: Compare solutions of different classifiers
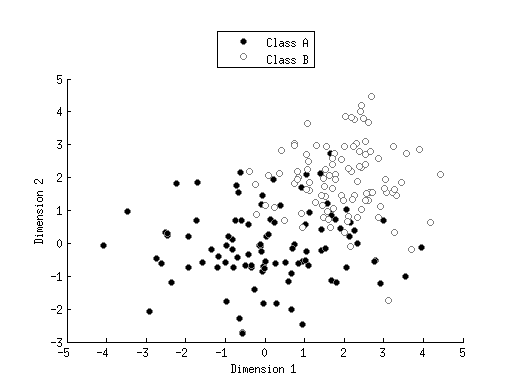
classA = bsxfun(@times,[1.5 1]',randn(2,100));
classB = 2+randn(2,100);
figure; hold on;
h1 = scatter(classA(1,:),classA(2,:),'ko','filled');
h2 = scatter(classB(1,:),classB(2,:),'wo','filled');
set([h1 h2],'MarkerEdgeColor',[.5 .5 .5]);
legend([h1 h2],{'Class A' 'Class B'},'Location','NorthOutside');
xlabel('Dimension 1');
ylabel('Dimension 2');
ax = axis;
xvals = linspace(ax(1),ax(2),200);
yvals = linspace(ax(3),ax(4),200);
[xx,yy] = meshgrid(xvals,yvals);
gridX = [xx(:) yy(:)];
X = [classA(1,:)' classA(2,:)';
classB(1,:)' classB(2,:)'];
y = [zeros(size(classA,2),1); ones(size(classB,2),1)];
paramsA = glmfit(X,y,'binomial','link','logit');
outputimageA = glmval(paramsA,gridX,'logit');
outputimageA = reshape(outputimageA,[length(yvals) length(xvals)]);
[d,hA] = contour(xvals,yvals,outputimageA,[.5 .5]);
set(hA,'LineWidth',3,'LineColor',[0 0 1]);
outputimageB = classify(gridX,X,y,'linear');
outputimageB = reshape(outputimageB,[length(yvals) length(xvals)]);
[d,hB] = contour(xvals,yvals,outputimageB,[.5 .5]);
set(hB,'LineWidth',3,'LineColor',[0 1 0]);
centroidA = mean(classA,2);
centroidB = mean(classB,2);
disttoA = sqrt(sum(bsxfun(@minus,gridX,centroidA').^2,2));
disttoB = sqrt(sum(bsxfun(@minus,gridX,centroidB').^2,2));
outputimageC = disttoA > disttoB;
outputimageC = reshape(outputimageC,[length(yvals) length(xvals)]);
[d,hC] = contour(xvals,yvals,outputimageC,[.5 .5]);
set(hC,'LineWidth',3,'LineColor',[1 0 0]);
legend([hA hB hC],{'logistic regression' ...
'linear discriminant analysis (LDA)' ...
'nearest-prototype classification'}, ...
'Location','NorthOutside');